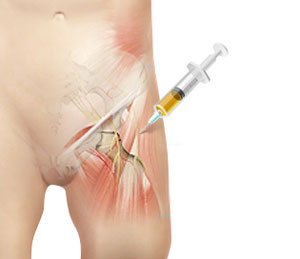
What is Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP)?
Our blood consists of a liquid component known as plasma. It also consists of three main solid components which include the red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets. Platelets play an important role in forming blood clots. They also consist of special proteins, known as growth factors, which help with our body’s healing process. Platelet-rich plasma or PRP is a high concentration of platelets and plasma. A normal blood specimen contains only 6% platelets, while platelet-rich plasma contains 94% of platelets and 5 to 10 times the concentration of growth factors found in normal blood, thus greater healing properties.
What are the Indications for PRP Injections?
PRP is a relatively new method of treatment for several orthopedic conditions such as muscle, ligament, and tendon injuries; arthritis; and fractures. PRP injections can help alleviate painful symptoms, promote healing, and delay joint replacement surgeries.
Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection Procedure
Your doctor will first draw about 10 cc’s of blood from the large vein in your elbow. The blood is then spun in a centrifuge machine for about 10 to 15 minutes to separate the platelets from the remaining blood components. The injured part of your body is then anesthetized with a local anesthetic. The platelet-rich portion of your blood is then injected into your affected area. In some cases, your doctor may use ultrasound guidance for proper needle placement.
Post-Operative Care following PRP Injections
It is normal to feel some discomfort at the injection site for a few days after your procedure.
- You will be prescribed pain medications by your doctor.
- You may use cold compresses to alleviate your symptoms.
- You will be instructed to stop any anti-inflammatory medications.
- You may resume your normal activities but should avoid any strenuous activities such as heavy lifting or exercises.
Risks and Complications of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections
- There are very minimal risks associated with PRP injections. Some of the potential risks include Increased pain at the injection site
- Infection
- Damage to adjacent nerves or tissues
- Formation of scar tissue
- Calcification at the injection site
The Role of PRP in both Nonsurgical and Surgical Tissue Healing
PRP is a promising and versatile therapy that can support and accelerate tissue healing in both non surgical and surgical scenarios. In nonsurgical settings, PRP can be injected into the injured site to reduce inflammation, pain, and swelling, and to promote tissue repair and regeneration. PRP can be used to treat various conditions, such as chronic wounds, ulcers, burns, sports injuries, tendinitis, and osteoarthritis. In surgical settings, PRP can be applied to the surgical site to enhance wound healing, reduce infection, and improve graft survival. PRP can be used to augment various procedures, such as skin grafts, bone grafts, cartilage repair, ligament reconstruction, and joint replacement.







